The Future of Smart Roads: AI, Sensors, and Real-Time Traffic Systems

As vehicles become smarter—with 4K dash cameras, ADAS, and connected in-car technologies—the roads beneath them must evolve too. The future of transportation isn’t just about autonomous cars; it’s about the smart infrastructure that will guide them. Across the world, governments and tech companies are building the next generation of smart roads, using artificial intelligence, advanced sensors, and real-time data to create safer, smoother, and more efficient travel.
At RoadTechHub, where we focus on the intersection between road innovation and vehicle technology, smart roads represent one of the biggest leaps in mobility we’ll see this decade. Here’s how they will reshape the way we drive.
What Are Smart Roads?
Smart roads are highways, motorways, and urban routes embedded with digital technologies that communicate with vehicles and traffic systems.



Their purpose is to:
- Reduce congestion
- Improve safety
- Lower emissions
- Provide real-time data
- Support AI-driven and autonomous vehicles
These roads use a combination of sensors, cameras, radar, edge computing, and AI software to create a constantly updated view of traffic and road conditions.
Think of them as the digital nervous system of future transportation.
The Core Technologies Powering Smart Roads
Smart roads rely on three major technological pillars: AI, sensors, and real-time traffic systems.
1. AI — The Brain Powering Road Intelligence

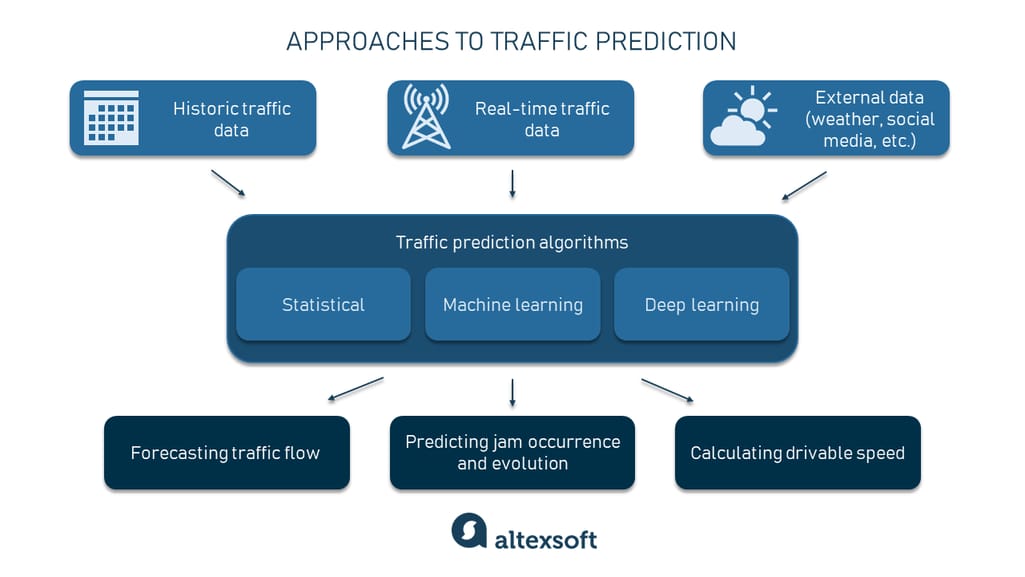

AI transforms raw data collected from the road into meaningful insights and automated actions.
How AI improves future roads:
- Predicting traffic flow before congestion forms
- Optimising traffic signals to improve travel times
- Detecting hazards instantly (stopped cars, debris, pedestrians)
- Supporting autonomous vehicle navigation
- Tracking environmental conditions and adjusting traffic management
AI gives roads the ability to think and respond.
2. Sensors — The Eyes and Ears of Smart Roads



Sensors gather constant live data that makes smart roads possible. They’re installed in:
- The asphalt
- Traffic signs
- Lampposts
- Road barriers
- Bridges
What these sensors detect:
- Vehicle speed & density
- Road temperature (helps detect black ice)
- Vibrations (accidents or harsh braking)
- Air pollution
- Snow, fog, and rain
- Pedestrian movement
They function like large-scale versions of the technology inside modern dash cameras and ADAS-equipped cars—always watching and analysing.
3. Real-Time Traffic Systems
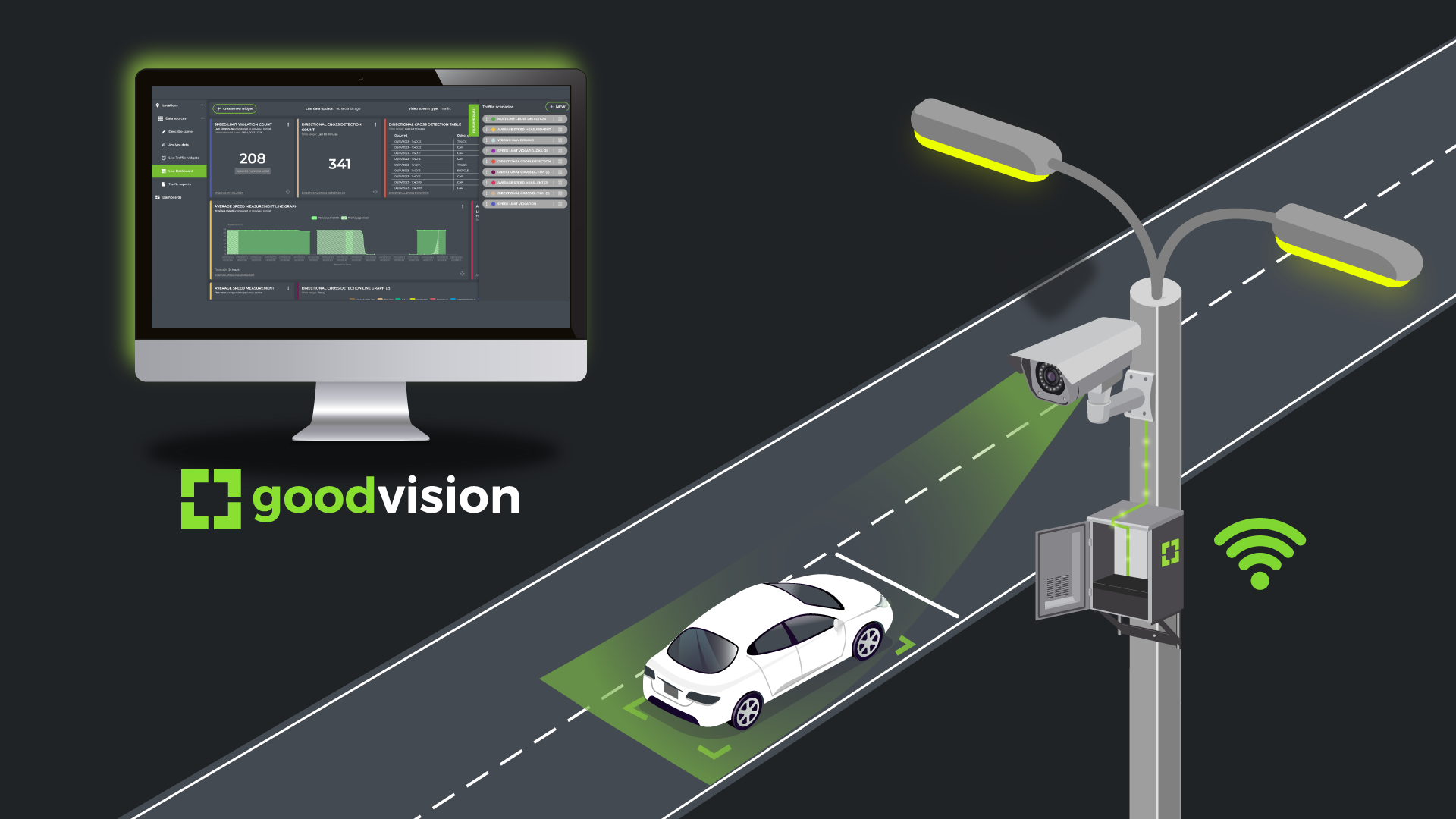


Real-time traffic systems create a live digital map of the road network, updating every second. They collect data from:
- Road sensors
- GPS signals
- Connected vehicles
- CCTV traffic cameras
- Weather stations
What real-time systems enable:
- Instant hazard alerts
- Faster route optimisation
- Adaptive speed limits
- Smarter navigation apps
- Dynamic lane usage
- Quick emergency response
This is the backbone of modern intelligent transportation.
How Smart Roads Improve Safety
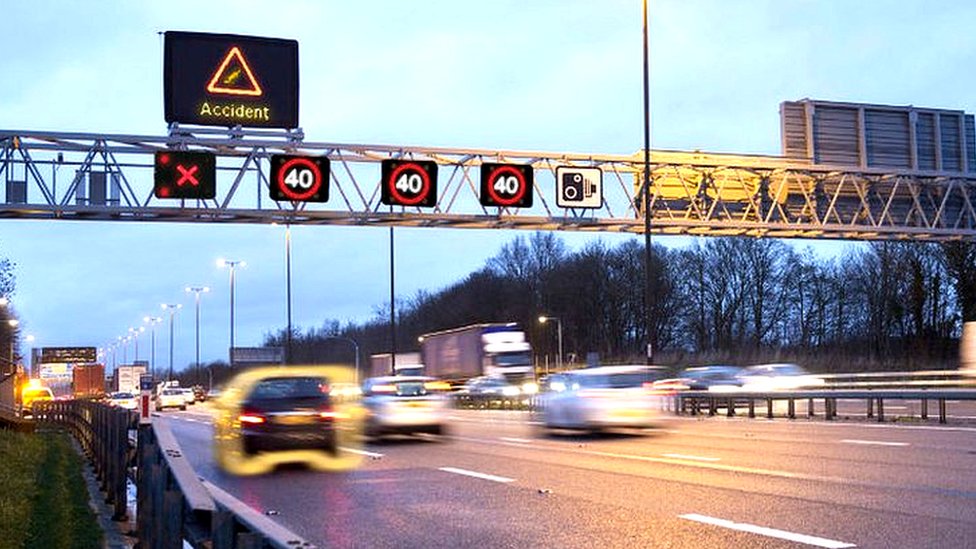



Smart roads dramatically increase safety by offering near-instant awareness of hazards.
Key safety benefits:
- Early hazard detection
Sensors detect accidents or stopped vehicles before traffic backs up. - Weather-based alerts
Roads warn drivers of ice, fog, or flooding. - Dynamic signage
Digital signs adjust speed limits and warnings automatically. - Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) communication
Cars receive alerts directly from the road:- “Debris ahead”
- “Sudden braking in your lane”
- “Pedestrian crossing detected”
Smart roads essentially give every driver a high-tech co-pilot.
Smart Roads & Autonomous Vehicles



Self-driving vehicles require more than onboard sensors—they need intelligent infrastructure to support them.
How smart roads support autonomy:
- HD mapping that updates itself
- Embedded lane guidance sensors
- Redundant safety layers
- Precise real-time data exchange
With smart roads, autonomous driving becomes safer, more predictable, and more energy-efficient.
Environmental Benefits of Smart Roads



Smart roads don’t just improve traffic—they benefit the planet.
Environmental advantages:
- Reduced congestion → lower CO₂ emissions
- LED smart streetlights that dim automatically
- Solar-powered road surfaces (in development)
- Optimised routing leading to less fuel waste
- Dynamic lanes reducing the need for road expansions
Cities adopting smart-road technology often see measurable climate improvements.
Challenges Ahead
While smart roads are promising, they come with obstacles:
- High installation costs
- Cybersecurity threats
- Data privacy concerns
- Long-term maintenance
- Need for global standards
However, as sensors and AI become cheaper, adoption will accelerate rapidly.
The Future Driving Experience
Imagine this scenario:
Your ADAS-equipped car joins the motorway.
Rain sensors reduce the speed limit.
Traffic slows 2 miles ahead—your car gets an automatic warning.
A stopped vehicle on the shoulder is detected, and your navigation adjusts instantly.
LED lane markers illuminate to guide traffic more safely.
This is the future of driving: smart cars on smart roads, working together to improve safety, efficiency, and comfort.
Final Thoughts (Tailored for RoadTechHub)
At RoadTechHub, we believe smart roads will transform mobility faster than any other road technology in the next decade. As vehicles adopt better dash cameras, more advanced ADAS systems, and eventually autonomous capabilities, the infrastructure beneath them will evolve in parallel.
Smart roads are not just the future—they are the foundation upon which future vehicle technology will rely.